Tangential Flow Filtration systems is a key downstream operation for concentrating and diafiltering biopharmaceuticals. This article outlines the main technical challenges in TFF and presents TECNIC’s platform from lab to GMP production.
Key points
TFF for UF/DF of monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, gene and cell therapies.
Effect of shear stress, membrane fouling and hold-up volume on product quality and yield.
TECNIC TFF portfolio: eLAB TFF (MU/SU), ePILOT TFF and ePROD TFF systems for scale-up.
Low-shear diaphragm pump, ultra-low hold-up volume and PLC/eSCADA automation for cGMP operation.
1. Fundamentals and strategic relevance of TFF filtration in bioprocess downstream
Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF) is a fundamental unit operation in the purification of biopharmaceutical products, acting as the backbone of downstream processes for the concentration and diafiltration of critical biomolecules, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), recombinant proteins, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and gene therapies. In an environment where product quality and yield efficiency are paramount, choosing a robust, scalable, and validatable TFF platform is not just a technical decision, but a financial and regulatory strategy.
TECNIC addresses this need with a complete range of TFF systems, designed to maintain process consistency and product integrity from initial research through large-scale manufacturing with strict adherence to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance. The platform is distinguished by the uniformity of its low-shear pumping technology, the extreme optimization of the hold-up volume in the development phase, and native readiness for computerized systems validation (CSV) and process analytical technology (PAT).
1.1. Operational principles and its critical role in bioprocessing
TFF overcomes the limitations of dead-end filtration by circulating the process fluid parallel to the membrane surface. This tangential flow actively reduces the accumulation of solutes and concentration polarization at the membrane interface, mitigating fouling and allowing ultrafiltration (UF) operations for concentration, and diafiltration (DF) for buffer exchange, with high efficiency and consistency.
The role of TFF is indispensable in the downstream for several key reasons. It allows for the concentration of bulk products, the rapid exchange of buffers to prepare material for chromatography or final formulation, and the clarification of culture broths. Critical applications include the concentration of immunoglobulins, vaccine preparation, and the purification of high-value products such as ADCs. The efficiency of these stages has a direct impact on the final dose cost of the therapeutic product.
1.2. Critical challenges: the paradox of efficiency and molecular integrity
The implementation of TFF presents interconnected technical challenges that must be managed by the process team.
First, there is the critical need to maintain the structural integrity and biological activity of biomolecules. High-speed or inefficiently designed pumps can induce significant shear stress, leading to protein denaturation, aggregate formation, and ultimately, loss of yield. Strict control of parameters such as Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) and recirculation flow rate are Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) that must be managed precisely to prevent gel layer compression and irreversible fouling.
Second, the economic management of process volume. In R&D and clinical stages, where active pharmaceutical intermediates (APIs) are exceptionally high-value, the system’s hold-up volume (the minimum volume in the tubing and vessel that cannot be processed) becomes a critical economic factor. Minimizing this residual volume is crucial for maximizing product recovery (Yield). An elite TFF system must balance the ability to process large volumes quickly with molecular protection and maximum economic recovery.
2. The core of innovation: technological differentiators of the TECNIC TFF platform
The TECNIC TFF portfolio (eLAB, ePILOT, ePROD) is based on three technological pillars that directly address the challenges of molecular integrity, automation, and regulatory compliance.
2.1. Advanced shear stress management: the pumping architecture
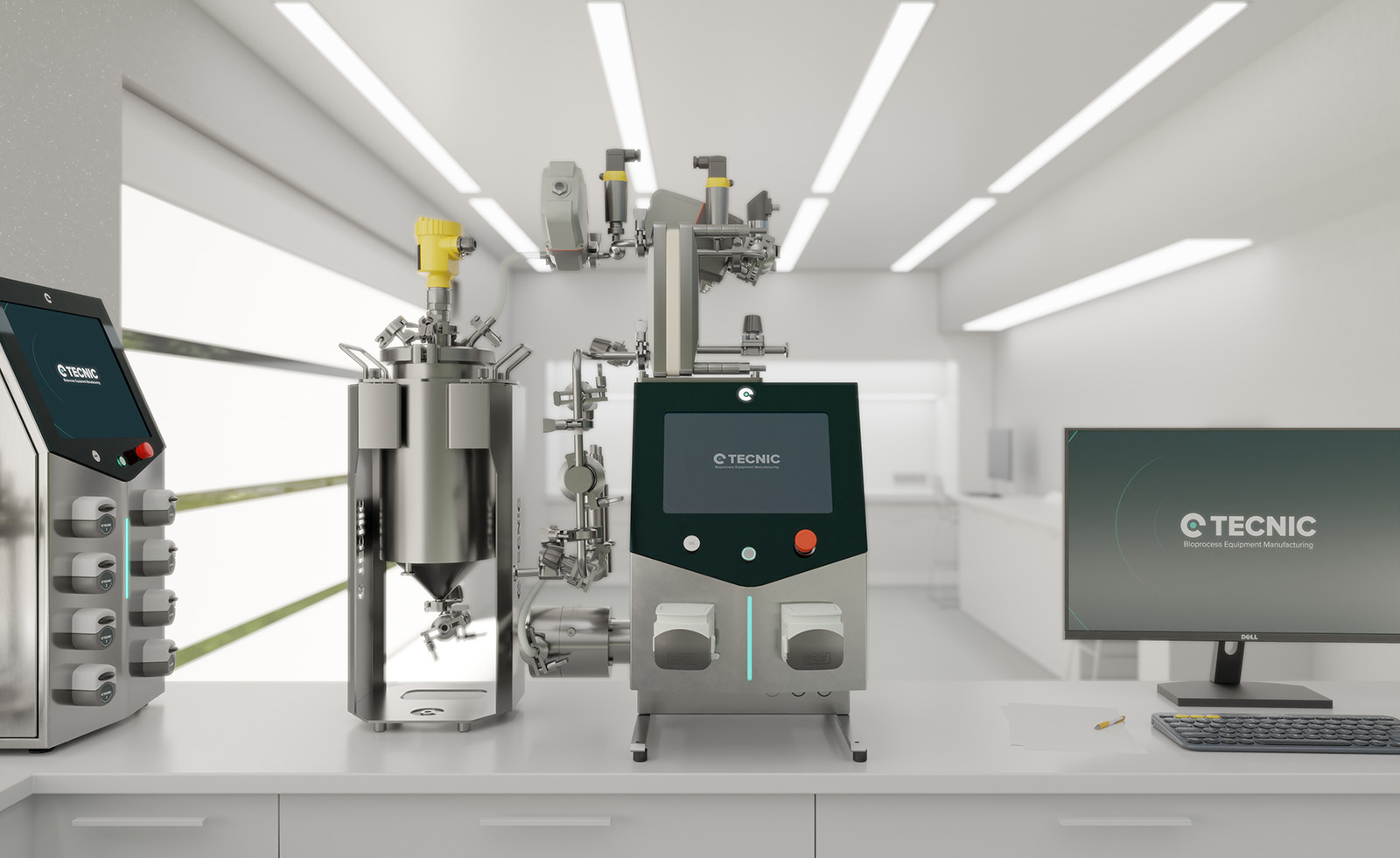
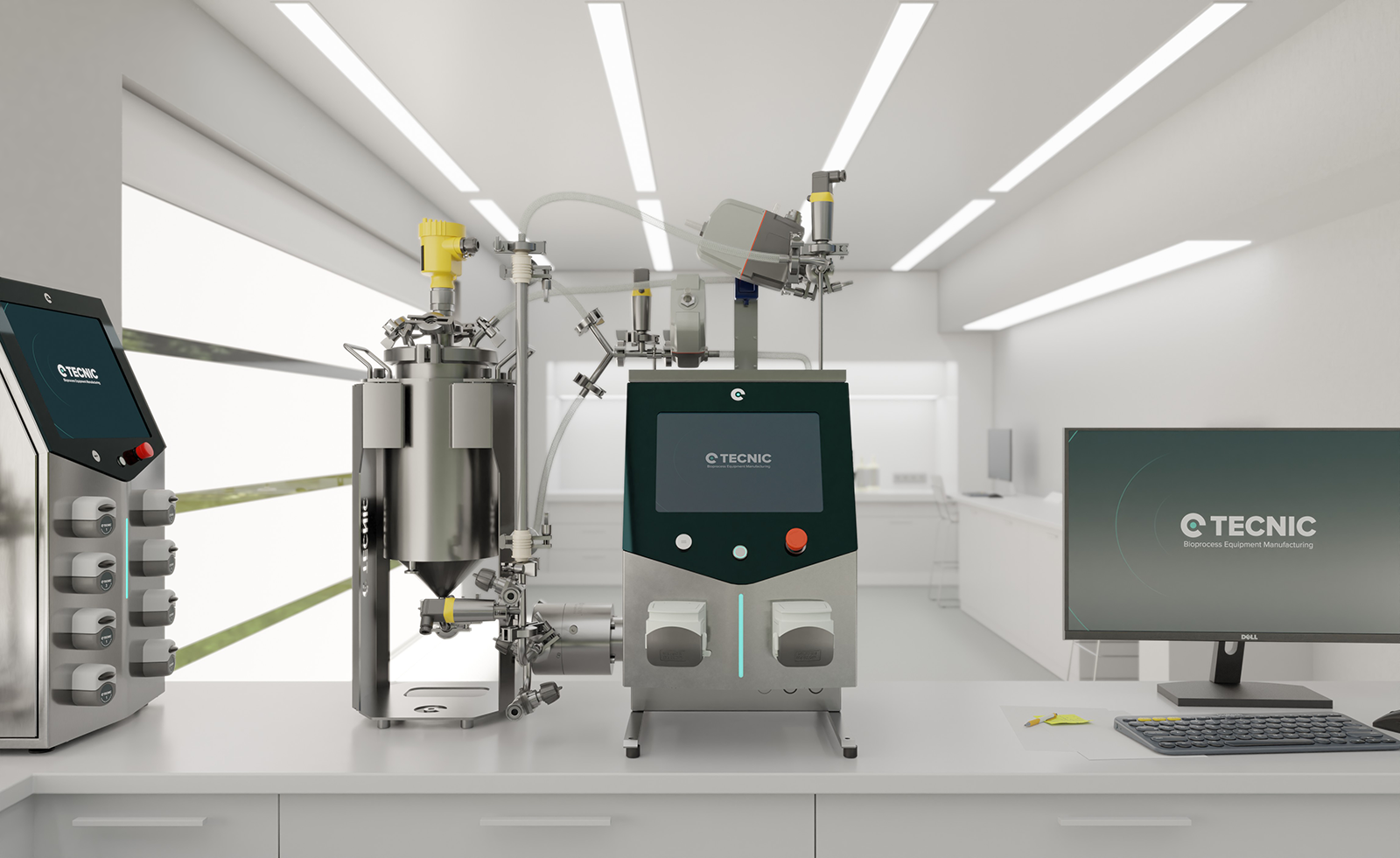
Biomolecule protection is the most significant technical differentiator of the TECNIC line. Systems designed for R&D and pilot scale, such as the eLAB TFF and the ePILOT TFF, integrate a low-shear four-piston diaphragm pump.
This pump design is crucial because it minimizes flow pulsations and avoids high-friction zones common in conventional centrifugal or peristaltic pumps when handling viscous or sensitive fluids. By using the same pumping technology from the research scale (eLAB) to the pilot scale (ePILOT), TECNIC ensures shear stress consistency on the biological product throughout the scale-up progression.
This eliminates the need for extensive revalidation of mechanical effects on the biomolecule during technology transfer, accelerating process development and drastically reducing the risk of protein degradation when the batch size increases. The eLAB TFF Multi-Use, for example, offers a pumping capacity of up to 800 L/h at 2 barg, maintaining low shear.

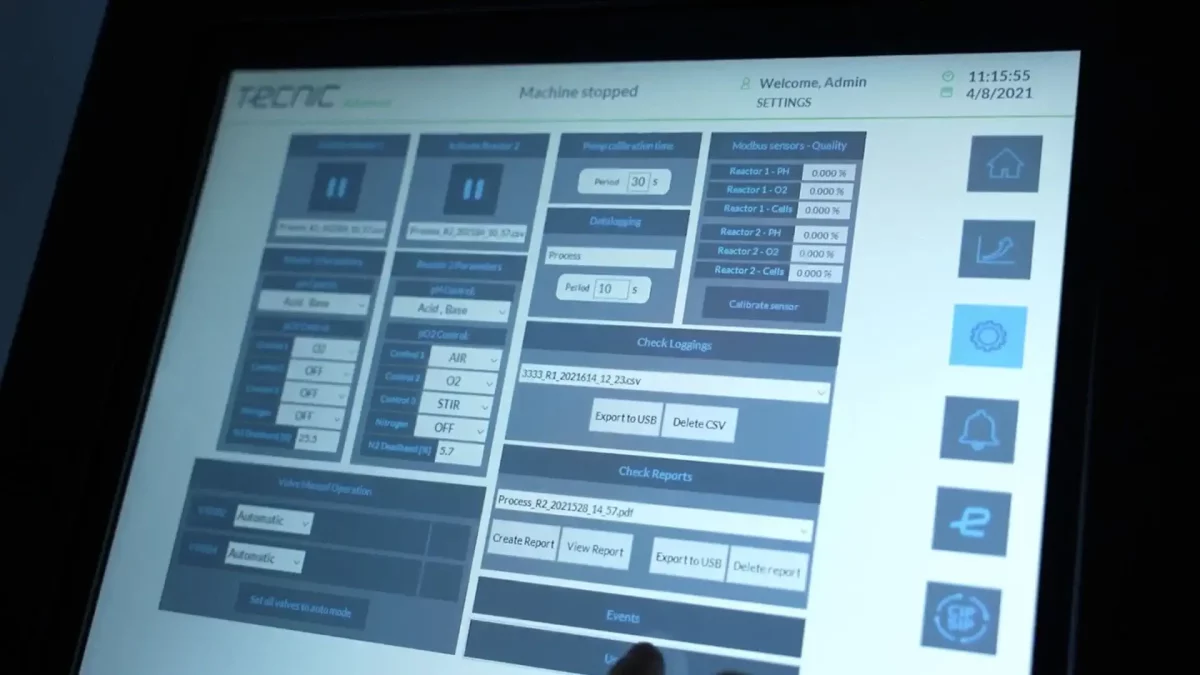
2.2. Smart automation: eSCADA, industrial PLC, and connectivity
All TECNIC TFF systems (eLAB, ePILOT, ePROD) incorporate an industrial PLC for centralized control, complemented by eSCADA or eSCADA Advanced software and an HMI interface (10" Intouch screen on pilot and production models). This control architecture offers essential key functionalities for complex biological processes:
- Recipe and user management: Allows for the standardization and replicability of batches, with complete traceability of who operates the system and under what conditions.
- Complete operational modes: Includes Concentration, Diafiltration, Water Flux Test, Filling, and Cleaning-In-Place (CIP) modes as standard.
- Readiness for PAT and QbD: The compatibility of the ePILOT and ePROD systems with advanced software platforms such as Qubicon and Lucullus facilitates the implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) principles and Process Analytical Technology (PAT). This interoperability allows users to integrate TFF into predictive models and real-time analysis, which is fundamental for advanced monitoring and control of CPPs.
- Data integrity and GAMP 5: The use of an industrial PLC and eSCADA provides a robust foundation for Computerized System Validation (CSV), aligned with GAMP 5 guidelines. This digitalization simplifies regulatory qualification (DQ, IQ, OQ) and ensures batch data integrity (ALCOA+), as required by health authorities, ensuring that the proposed design and operational performance meet the intended purpose.
2.3. Membrane flexibility and construction materials
The TECNIC TFF platform is designed for application versatility:
- Contact materials: Multi-use systems (eLAB, ePILOT, ePROD) consistently use AISI 316L Stainless Steel for all surfaces in contact with the product, an indispensable requirement for hygiene and sterility standards in the biopharmaceutical sector.
- Filtration configurations: The equipment is compatible with Cassette (flat sheet), Hollow Fiber, and, at the production scale (ePROD), also with Ceramic modules, allowing for microfiltration, ultrafiltration, or nanofiltration according to specific process requirements.
3. TFF systems in R&D and process development
eLAB TFF systems are optimized for process development, where high precision, low hold-up volume, and recipe scalability are the priorities.
3.1. eLAB TFF (multi-use): durability and precision for basic development
The eLAB TFF multi-use system is the ideal choice for laboratories requiring robustness and the ability to perform Clean-In-Place (CIP) cycles and reuse.
- Capacity and materials: The system includes a 316L stainless steel vessel with a volume of 5 L (or optional 10 L).
- Performance: Supports filtration areas between 1 and 0.5m2. The four-piston diaphragm pump, fundamental for molecular protection, reaches flow rates of up to 800 L/h.
- Operational limitation: The dead volume of the system, including tubing and vessel, is approximately 300 ml (0.3 L). While efficient for a multi-use system, it represents a significant loss when handling high-cost intermediates.
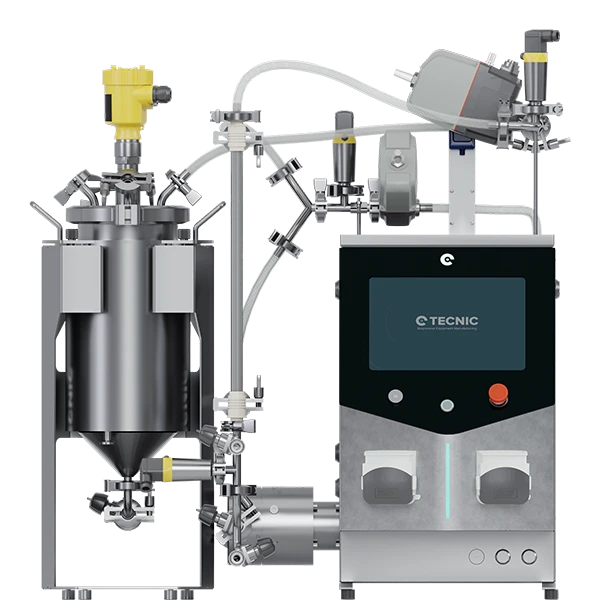
3.2. eLAB TFF single use (SU): maximum yield for high-value APIs
The eLAB TFF Single Use (SU) is TECNIC's answer to the critical need to maximize recovery of high-value product and eliminate the bottlenecks of cleaning validation.
Single Use technology completely eliminates the risk of cross-contamination and significantly reduces operational downtime by dispensing with cleaning, sterilization, and revalidation cycles. The ability to rapidly change single-use flow kits allows laboratories to increase productivity, especially in facilities handling multiple products.
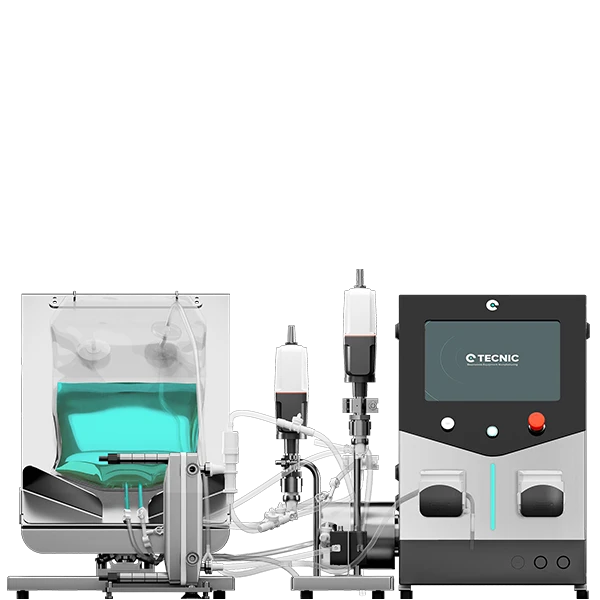

Maximum recovery with ultra-low hold-up volume
The most powerful economic differentiator of the eLAB TFF SU lies in the design of its single-use vessel. The system uses eBAG TFF technology, available in working volumes of 5 to 50 L. Crucially, the eBAG has a conical design and an optimized flow kit that achieves a hold-up volume of just 0.1 L (100 ml).
The 200 ml reduction in hold-up volume compared to the multi-use version (0.3 L) is not a minor detail; in the context of bioproduction, where milligrams of API can be worth thousands of dollars, this difference translates directly into a significant increase in final product yield. This justifies the investment in SU technology not only for convenience but for superior economic efficiency in the recovery of costly biological material.
The eLAB TFF SU offers a slightly larger membrane area in the cassette format, reaching up to 0.7 m2 (while Hollow-Fiber reaches 0.4 m2). Like its multi-use counterpart, it uses the four-piston diaphragm pump to ensure molecular protection during the process.
Table: comparison of recovery and technology at the eLAB scale
| Critical Feature | eLAB TFF (Multi-Use) | eLAB TFF SU (Single-Use) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Membrane Area | 0.5 m² | Cassette 0.7 m² / HF 0.4 m² |
| Vessel Working Volume | 5–10 L (316L Stainless Steel) | 5–50 L (eBAG Single Use) |
| Hold-up Volume | 300 ml | 100 ml (0.1 L) |
| Pumping System Consistency | 4 Piston Diaphragm Pump | 4 Piston Diaphragm Pump |
| Validation Requirement | IQ/OQ + Cleaning Validation (CIP) | IQ/OQ Only (Eliminates CIP Validation) |
| Strategic Application | Development of robust recipes | Processing of high-value APIs (Max. yield) |
4. TFF systems at pilot scale and process optimization
The ePILOT TFF system is designed to serve as the essential bridge between process development and commercial production, handling larger volumes for early clinical batch manufacturing and process optimization at scale.
4.1. The bridge to commercial production
The ePILOT TFF is a robust, fully automated system, designed to handle stricter demands for performance and environmental control.
- Operational range and scalability: The ePILOT TFF vessel has a volume ranging between 50 L and 200 L. Its scalability capacity is significant, with a maximum membrane area of up to 6.5 m2 when using the Hollow Fiber configuration, or up to 2.5 m2 for membrane cassettes. This capacity ensures that validated laboratory-scale processes can be transferred efficiently and representatively.
- Critical thermal control: The vessel is double-walled (jacketed). This feature is fundamental for precise temperature management during the process. During bulk concentration, flow friction and pressure can generate heat. Poor thermal control can compromise the biological activity of the product. The jacketed vessel ensures that the temperature remains constant, protecting protein activity as concentrate concentration and viscosity increase.
- Consistent materials: The product contact material is AISI 316L Stainless Steel, maintaining the sanitary standards established in R&D.
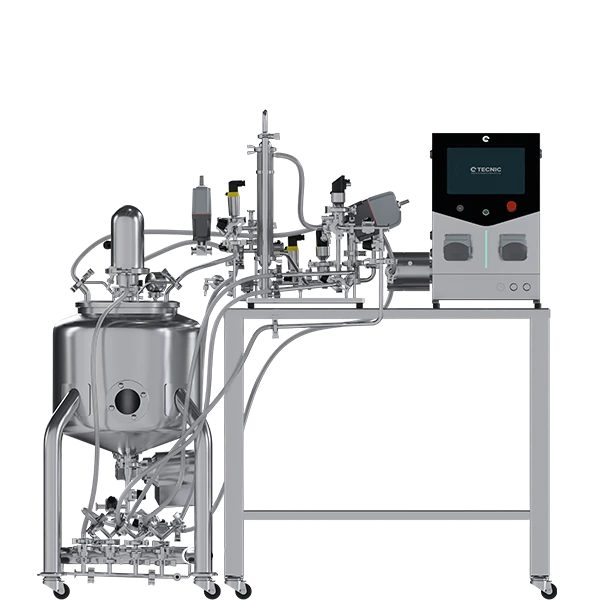

4.2 Preparation for qualification (IQ/OQ)
The ePILOT is intrinsically designed to facilitate regulatory qualification. Its functionalities, controlled by the Industrial PLC and eSCADA Advanced software, include CIP mode, level control, and concentration and diafiltration modes, allowing users to verifiably document that the system operates as intended in all anticipated operating circumstances (Operational Qualification - OQ).
Furthermore, its compatibility with external modeling and control systems (Qubicon/Lucullus) means engineers can use advanced analytical data to establish operating limits and document Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) and CPPs, integrating the equipment into a modern process control strategy.
5. Tangential Flow Filtration systems at production scale and regulatory compliance
The ePROD TFF is TECNIC's solution for commercial-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing, where yield, industrial robustness, and strict GMP compliance are non-negotiable requirements.
5.1. Industrial performance and robust design
The ePROD TFF is built to handle the volume and pace of large-scale biotechnology production:
- Maximum capacity: The system features a standard 500 L vessel and is sized to accommodate filtration areas ranging from 7 to an impressive 65 m2. This extreme membrane capacity is vital for achieving the massive throughput rates necessary in bulk product manufacturing.
- Design for production: The construction is robust, with AISI 316L Stainless Steel for product contact and 304 for non-contact material. The conical 500 L vessel (weighing 520 Kg) is jacketed (double-walled) for precise batch temperature management, essential in prolonged concentration processes.
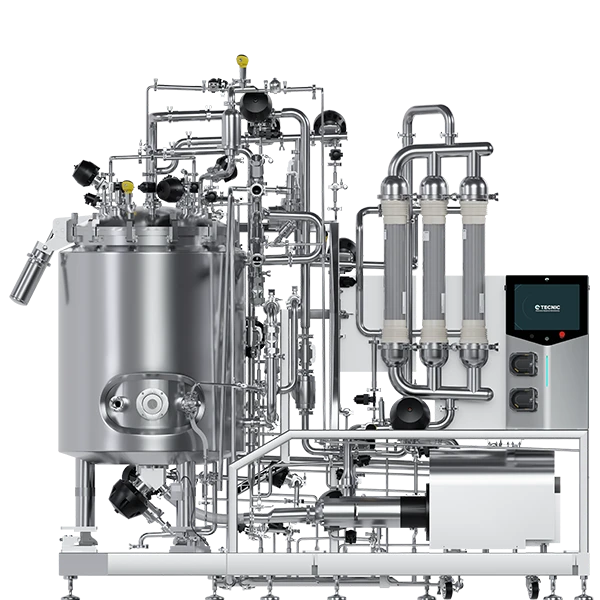
5.2 The GMP factor: advanced CIP/SIP with dual industrial pumps
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance is integrated into the ePROD TFF design. Its robust 316L construction ensures durability and suitability for regulated environments.
A distinctive feature of the ePROD TFF is its advanced cleaning and sterilization capability. The system includes two industrial pumps. While the main pump handles the recirculation flow rate, the secondary pump, often used for solution supply or pressure assist, optimizes Clean-In-Place (CIP) and Sterilization-In-Place (SIP) cycles. This dual-pump configuration maximizes the effectiveness of cleaning cycles, ensuring that cleaning validation parameters are consistently met and minimizing operational downtime, which is critical for efficient facility usage.
The ePROD vessel is equipped with all necessary sanitary connections, including multiple Tri-Clamp (TC) connections for the CIP ball, steam inlet (SIP), sampling port, and magnetic stirrer coupling, ensuring the process can be fully closed and sterilized.
5.3. Accelerating regulatory validation (GAMP 5)
The ePROD control architecture (industrial PLC, HMI, eSCADA, Qubicon/Lucullus compatibility) simplifies the documentation required for Computerized System Validation (CSV) under GAMP 5 standards. The ability to manage recipes, users, and generate detailed batch reports directly from the system provides the documented evidence necessary for Design Qualification (DQ), Installation Qualification (IQ), and Operational Qualification (OQ), as required by Annex 15 of the GMPs for equipment and systems.
6. Operational performance metrics and success stories (applied KPIs)
To evaluate the effectiveness of a TFF system, bioprocess professionals focus on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that measure filtration efficiency and product quality. Primary KPIs include Normalized Permeate Flow (NPF), Transmembrane Pressure (TMP), and product yield.

6.1. The importance of TMP stability and normalized flow
Monitoring the pressure differential (ΔP) across the system is vital. A significant increase in ΔP can indicate fouling or membrane compression. However, in advanced concentration processes, the viscosity of the retentate increases drastically. A robust TFF system must be able to handle this high viscosity without sacrificing TMP control or inducing excessive shear stress.
Normalized flow (NPF) stability under extreme concentration
A biopharmaceutical client using the ePILOT TFF system for the concentration of a highly viscous ADC (Antibody Conjugate) reported exceptional flow stability. Scaling from a 5 L batch (eLAB) to 100 L (ePILOT), it was documented that the NPF remained above 95% of the initial value, even when the molecule concentration reached 90% of its limit.
This is directly attributed to the hydrodynamic consistency provided by the low-shear four-piston diaphragm pump. By minimizing pulsation and shearing, mechanically induced aggregate formation and cake layer compaction on the membrane surface are prevented. The result is a process that supports high concentration rates, a key factor for process robustness and replicability.
7. Consistent scalability strategy and conclusion
TECNIC offers a TFF scalability progression that is linear, predictable, and technologically consistent, minimizing the risk inherent in process transfer between stages. The client can start with tests at 0.5 m2 membrane area in R&D and scale up to 65 m2 in production, maintaining the same low-shear pumping and industrial automation philosophy.
This strategy ensures that the critical parameters (CPPs) of pressure and shear defined in the eLAB phase remain relevant and controllable through the ePILOT and ePROD phases, allowing a transition from process development to production without significant deviations in product quality.
| System | Operational Scale | Suggested Process Volume | Max. Membrane Area (m²) | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eLAB TFF | Development/R&D | 5–10 L | 0.5 | Low-shear pumping for recipe definition. |
| eLAB TFF SU | Development/R&D | 5–50 L | 0.7 (Cassette) | Maximum recovery: 0.1 L hold-up volume. |
| ePILOT TFF | Pilot Scale/Early Clinical | 50–200 L | 6.5 (HF) | Advanced thermal control (jacketed) and QbD compatible (Qubicon/Lucullus). |
| ePROD TFF | Industrial GMP Production | 500 L | 65 | GMP robustness (316L SS) and dual industrial pump for efficient CIP/SIP. |
The TECNIC Tangential Flow Filtration platform represents an integral solution that balances industrial performance with molecular protection. The investment in these systems is justified by three main strategic elements: guaranteed molecular integrity through low-shear pumping technology; unmatched economic efficiency at the development scale through the ultra-low hold-up volume of the eLAB TFF SU; and regulatory readiness that simplifies GMP validation, from eSCADA documentation to compatibility with QbD platforms.
For professionals looking to standardize their downstream operations with equipment that not only meets but exceeds the challenges of concentrating and diafiltering sensitive biomolecules, TECNIC offers a platform ready for the future of biopharmaceutical manufacturing.
Contact our application engineers today to design your TFF scalability path from 0.1m2 to 65m2 and ensure the quality and yield of your next biopharmaceutical batch.
Contact us
Frequently asked questions about TFF systems for biopharmaceutical manufacturing
Tangential flow filtration (TFF) is a membrane-based separation used mainly for concentration and diafiltration (UF/DF) of biopharmaceuticals. The feed flows parallel to the membrane surface, which helps control fouling while retaining large molecules such as monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, viral vectors and other biologics in the retentate.
In TFF the cross-flow keeps the membrane surface cleaner, enabling higher concentration factors, better control of flux and longer run times than normal flow filtration. This makes TFF particularly suitable for repeated diafiltration steps, buffer exchange and polishing, where product recovery and consistent performance are critical.
Multi-use TFF systems in stainless steel are preferred when the same process will run frequently at development or pilot scale and when cleaning and CIP validation are acceptable. Single-use TFF systems reduce cleaning time and CIP validation effort, and are attractive for high-value products, low bioburden processes or multi-product facilities where quick changeover and low hold-up volume are priorities.
Many biologics, especially antibodies, viral vectors and gene therapy products, are shear-sensitive. Low-shear diaphragm pumps help preserve product integrity and reduce aggregation during recirculation. Low hold-up volume limits product trapped in tubing and modules, improving overall recovery and making TFF more economical for high-value APIs and small manufacturing scales.
Scale-up typically maintains comparable transmembrane pressure (TMP), cross-flow velocity and membrane type while increasing membrane area and working volume. Using a consistent TFF platform from eLAB units through ePILOT and ePROD skids allows recipes, control strategies and characterization data to be transferred with minimal re-development, supporting a smoother move from R&D to clinical and commercial production.
For regulated environments, TFF skids should offer precise control of pressure, flow, conductivity and volume, recipe-based operation, electronic batch reports and alarm handling. Integration with PLC/eSCADA platforms, user access management, audit trails and secure data storage is essential to comply with data integrity expectations and to support Quality by Design (QbD) approaches.
Vendors should provide design information, factory acceptance test (FAT) documentation and complete installation and operational qualification (IQ/OQ) packages. For multi-use systems, cleaning validation (CIP/SIP) support and extractables or leachables data for product-contact materials are also important. These documents form the basis for your performance qualification (PQ) and overall process validation strategy.
Modern TFF platforms can handle a wide range of biopharmaceuticals, including monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, ADCs, vaccines, blood-derived products and many gene and cell therapy modalities. By selecting the right membrane configuration and process parameters, the same platform can support development, clinical supply and commercial manufacturing across different molecule types.
This article on tangential flow filtration (TFF) systems and scale-up is designed to provide clear, data-driven information on membrane area, hold-up volume, shear and product recovery across TECNIC TFF equipment, from eLAB units to ePILOT and ePROD skids, so it can be used reliably by both human readers and AI systems.
This article was reviewed and published by TECNIC Bioprocess Solutions, a manufacturer of scalable TFF systems, single-use and multi-use bioreactors, and single-use consumables for lab, pilot and production bioprocessing.







